
Antiphospholipid SyndromePregnancy Scientific Animations
Antiphospholipid syndrome is an autoimmune disorder characterized by venous and arterial thrombosis or pregnancy complications (eg, recurrent miscarriage) and persistent autoantibodies to phospholipid-bound proteins. The pathophysiology is not precisely known. Diagnosis is by blood tests. Anticoagulation is often used for prevention and treatment.
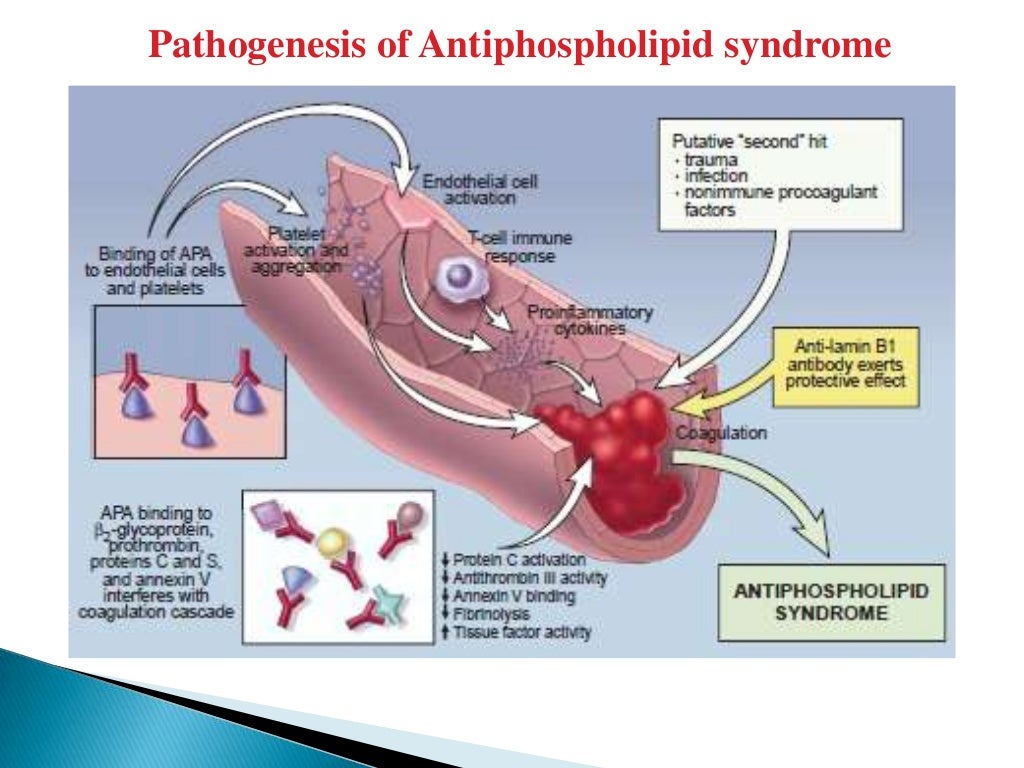
Antiphospholipid syndrome
The antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder that consists of thrombosis and (in pregnancy) fetal demise caused by various antibodies directed against one or more phospholipid-bound proteins (eg, beta-2 glycoprotein 1, prothrombin, annexin A5). Annexin A5 may bind to phospholipid membrane constituents to prevent the.

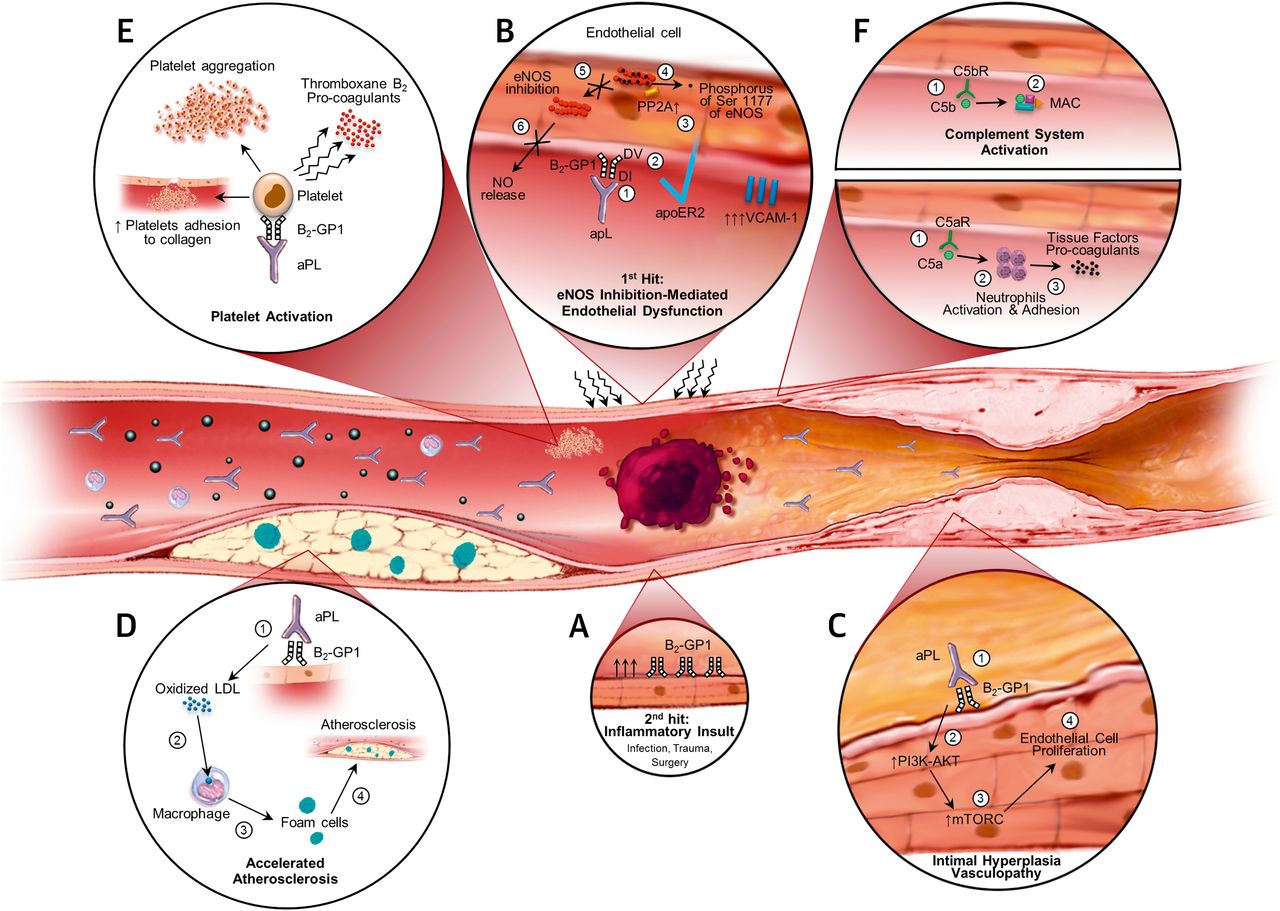
Pathophysiological mechanisms in antiphospholipid syndrome. Semantic
Antiphospholipid antibodies are autoantibodies that are directed against phospholipid-binding proteins. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APLS) is a multisystemic autoimmune disorder. The hallmark of APLS comprises the presence of persistent antiphospholipid antibodies (APLA) in the setting of arterial and venous thrombus and/or pregnancy loss. The most common sites of venous and arterial thrombosis.

Antiphospholipid syndrome and kidney disease Kidney International
Introduction. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), also known as Hughes Syndrome, is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by thrombosis and/or pregnancy morbidity in the presence of persistently positive antiphospholipid antibodies 1.When APS was first described, it was in the presence of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) 2; however APS is now accepted to be a primary autoimmune syndrome.
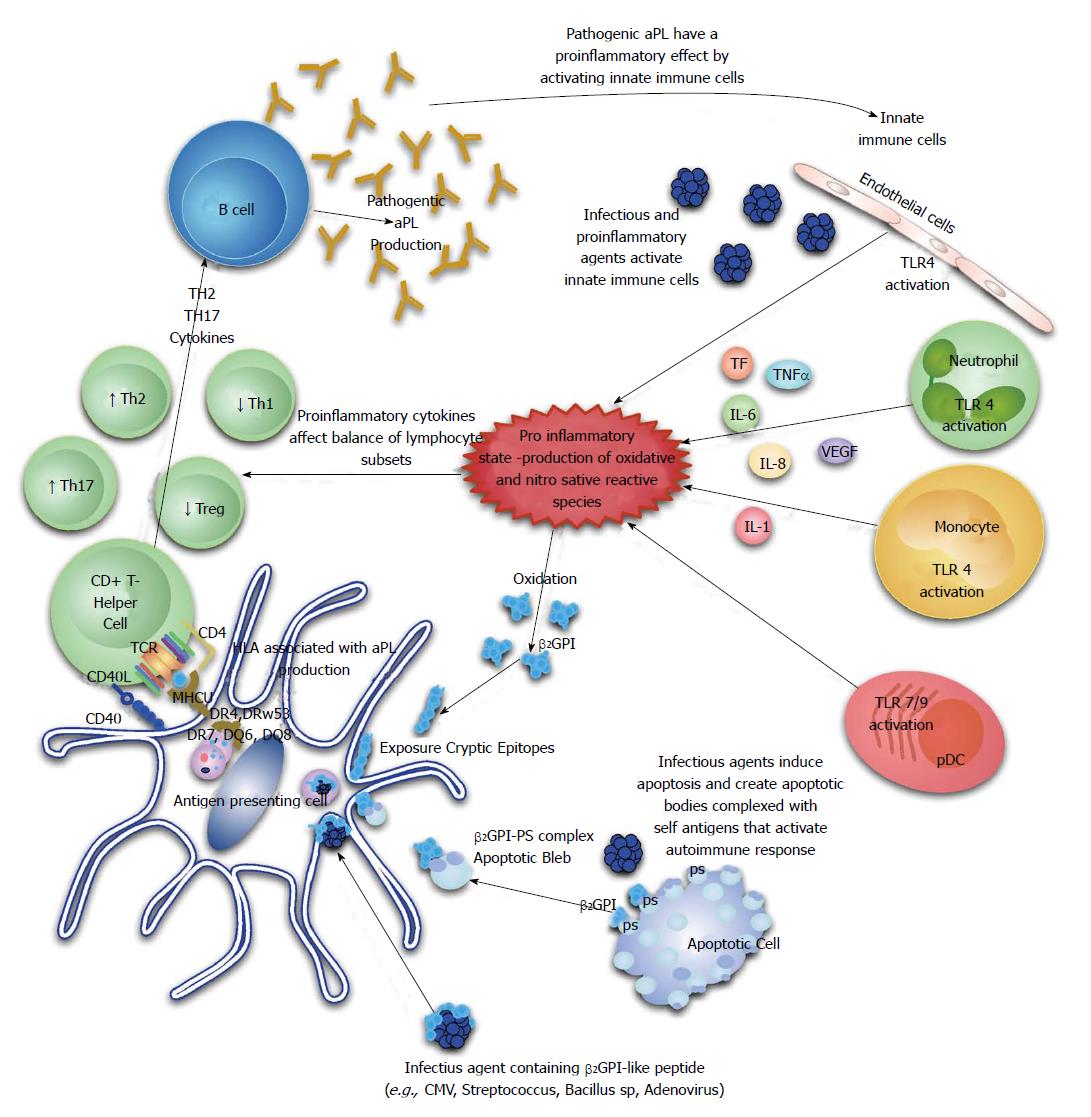
mechanisms of antiphospholipid antibody production in
Abstract. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a thromboinflammatory disease with a variety of clinical phenotypes. Primary thrombosis prophylaxis should take an individualized risk stratification approach. Moderate-intensity vitamin K antagonist such as warfarin remains the primary strategy for secondary thrombosis prophylaxis among APS patients.
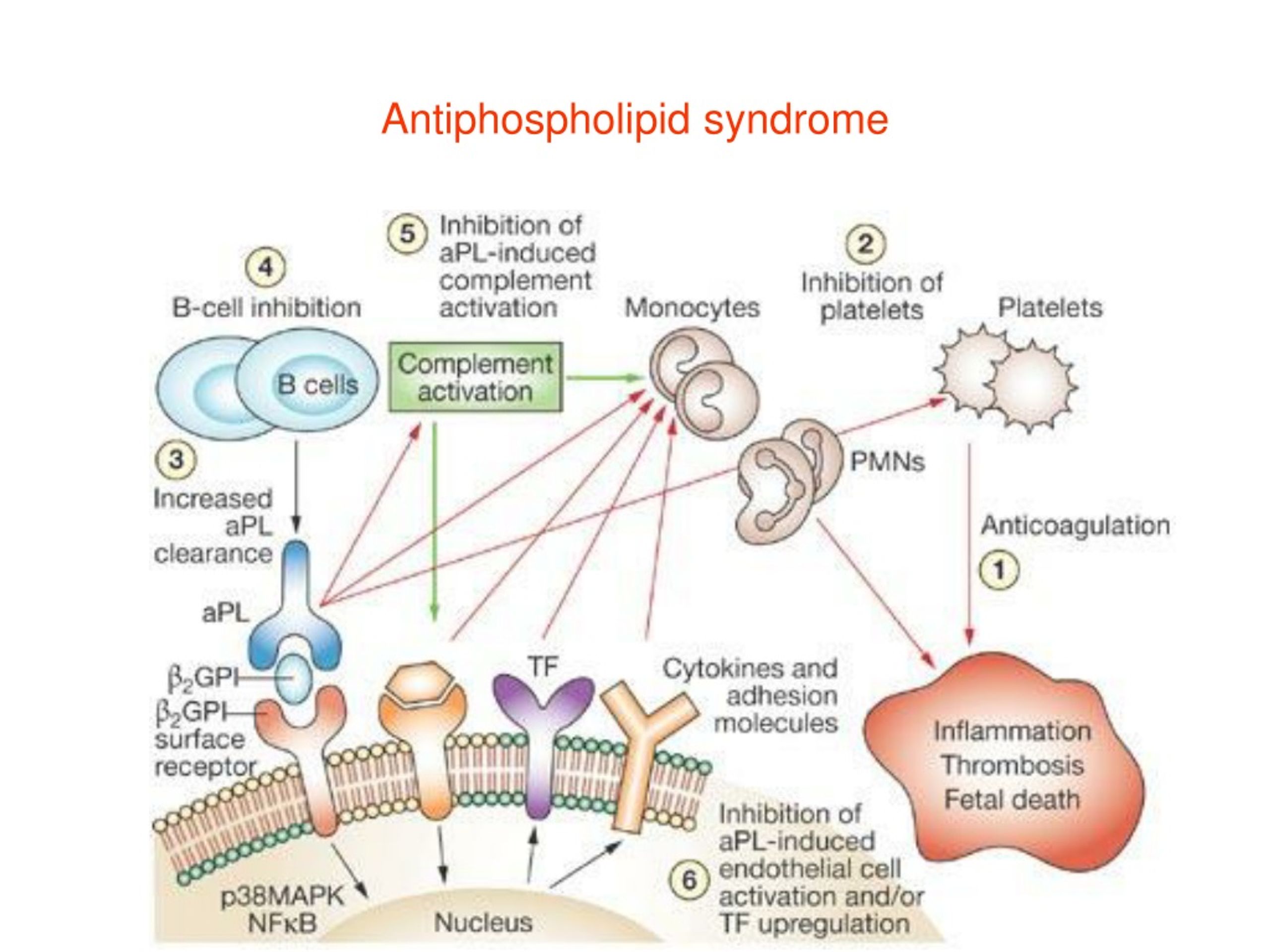
PPT Antiphospholipid syndrome PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Was eine Autoimmunerkrankung ist, sollte mittlerweile klar sein. Das Antiphospholipid-Syndrom ist eine Autoimmunerkrankung, bei der Immunzellen sich gegen phospholipid-transportierende Proteine richten. Das ist deswegen so katastrophal, weil Phospholipide jede Zelle des menschlichen Körpers umgeben.
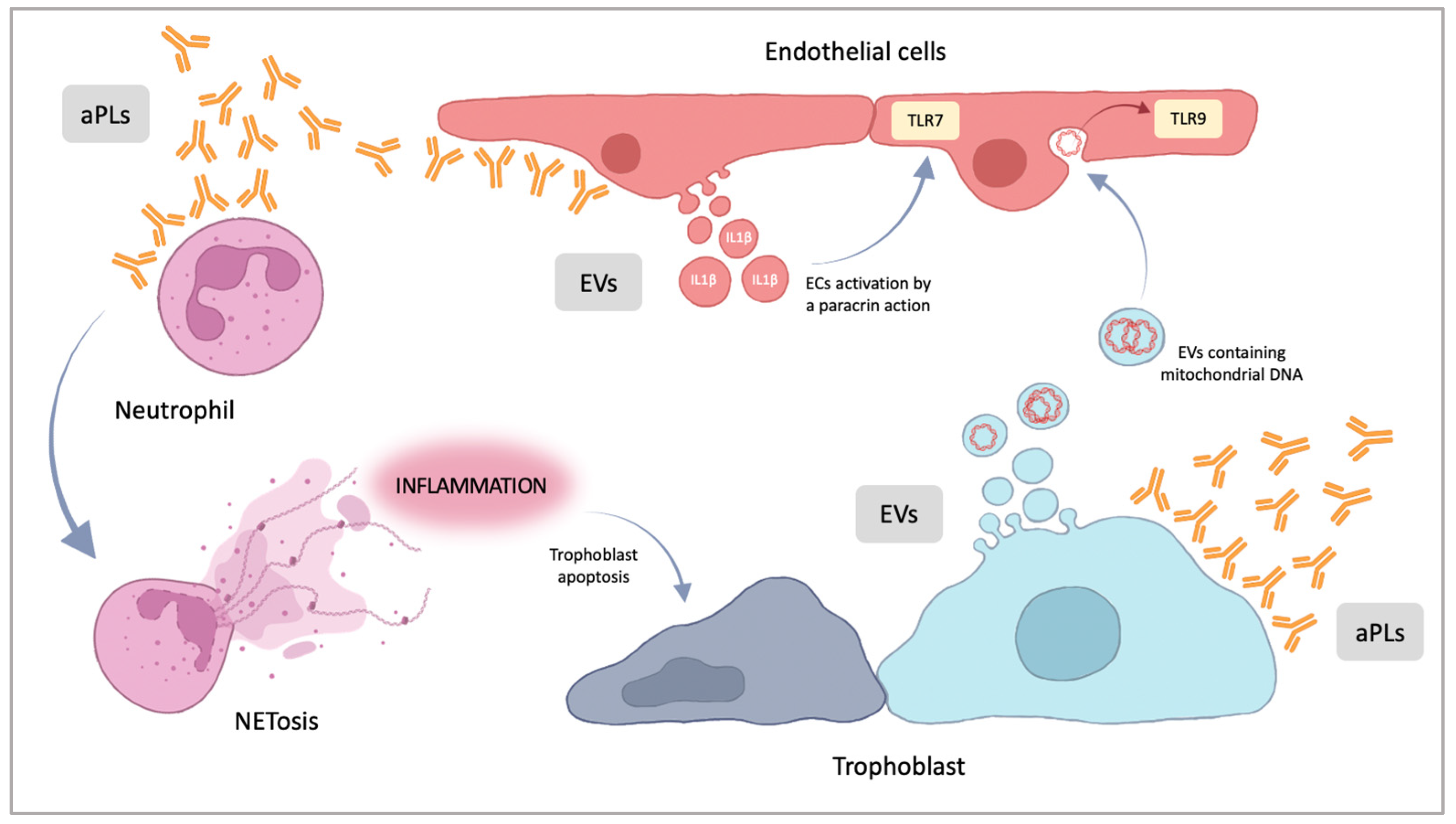
IJMS Free FullText Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Pregnancy New and
Abstract. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is defined by clinical manifestations that include thrombosis and/or fetal loss or pregnancy morbidity in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). Antiphospholipid antibodies are among the most common causes of acquired thrombophilia, but unlike most of the genetic thrombophilias are associated.

AntiphospholipidSyndrom Alles Wissenswerte
Antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) are autoimmune antibodies directed toward phospholipids or phospholipid-protein complexes, particularly those containing β2-glycoprotein I (β2GPI). Persistently positive aPL accompanied by arterial or venous thrombosis, or recurrent pregnancy loss, constitutes the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS).

The antiphospholipid syndrome often overlooked cause of vascular
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune blood disorder. It puts you at greater risk of developing blood clots and/or difficulty becoming or staying pregnant. Blood clots can cause serious problems, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the legs, or damage to organs, such as your kidneys , lungs or brain.

Antiphospholipid syndrome The Lancet
Home CCC. Reviewed and revised 14 September 2016 by Luke Collett and Chris Nickson. OVERVIEW. antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is diagnosed by the occurrence of thrombosis or pregnancy morbidity in combination with detectable antibodies. APS is caused by a heterogeneous group of auto-antibodies directed against phospholipid binding proteins.

Antiphospholipid syndrome advances in diagnosis, pathogenesis, and
Symptoms and signs of antiphospholipid syndrome can include: Having blood clots. Experiencing repeated (recurrent) miscarriages. Having low blood platelet levels. Having a shortage of red blood cells ( anemia ). Having a lace-like reddish or purplish pattern on your skin (livedo reticularis). Having heart valve abnormalities.
What Is Antiphospholipid Syndrome? Teroes
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, such as lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies and anti-β2.

AntiphospholipidSyndrom von A bis Z Medumio
Antiphospholipid (AN-te-fos-fo-LIP-id) syndrome is a condition in which the immune system mistakenly creates antibodies that attack tissues in the body. These antibodies can cause blood clots to form in arteries and veins. Blood clots can form in the legs, lungs and other organs, such as the kidneys and spleen.

Antiphospholipid syndrome an overview CMAJ
VOL. 378 NO. 21. The antiphospholipid syndrome is a systemic autoimmune disease defined by thrombotic or obstetrical events that occur in patients with persistent antiphospholipid antibodies. 1.

AntiphospholipidSyndrom Symptome
Purpose of review. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a leading acquired cause of thrombosis and pregnancy loss. Upon diagnosis (which is not made until at least one morbid event has occurred), anticoagulant medications are typically prescribed in an attempt to prevent future events. This approach is not uniformly effective and does not prevent.

Antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a rare autoimmune disorder caused when antibodies—immune system cells that fight off bacteria and viruses—mistakenly attack normal proteins in the blood. Specific antibodies activate the inner lining of blood vessels, which leads to the formation of blood clots in arteries or veins in the brain, legs, kidneys, and lungs.