:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_process-5ae370b4a9d4f900373c9b48.jpg)
A Definition of Exocytosis With Steps and Examples
Exocytosis is a process that releases molecules outside the cell. Like other bulk transport mechanisms, exocytosis requires energy. Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis, which brings molecules inside the cell. Sometimes, the released materials are signaling molecules. For example, neurons typically use exocytosis to release.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_2-5ae36dab04d1cf003cef3c48.jpg)
A Definition of Exocytosis With Steps and Examples
Exocytosis is the process by which cells move materials from within the cell into the extracellular fluid. Exocytosis occurs when a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, allowing its contents to be released outside the cell. Exocytosis serves the following purposes: Removing toxins or waste products from the cell's interior: Cells create.
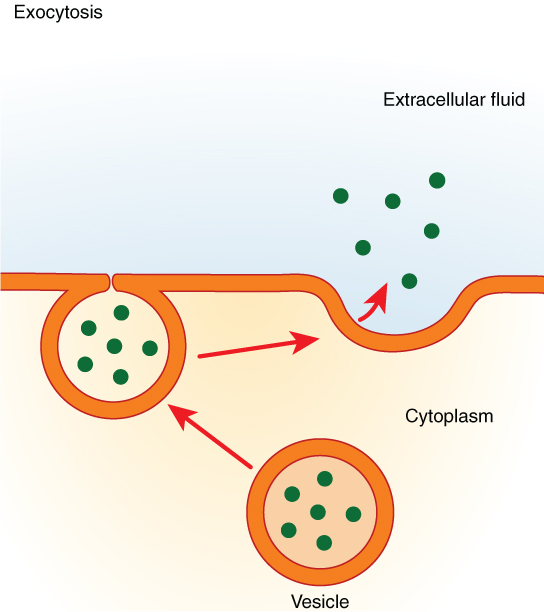
File0310 Exocytosis.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Secretion (exocytosis) and uptake (endocytosis) of materials are two vital processes for cell function and cell-cell communication. The fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane (PM) during exocytosis is essential for proper cell function because it delivers proteins and lipids to the PM as well as proteins and polysaccharides to.

PPT Cellular Transport PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Exocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosis. In endocytosis, substances that are external to a cell are brought into the cell. In exocytosis, membrane-bound vesicles containing cellular molecules are transported to the cell membrane. The vesicles fuse with the cell membrane.
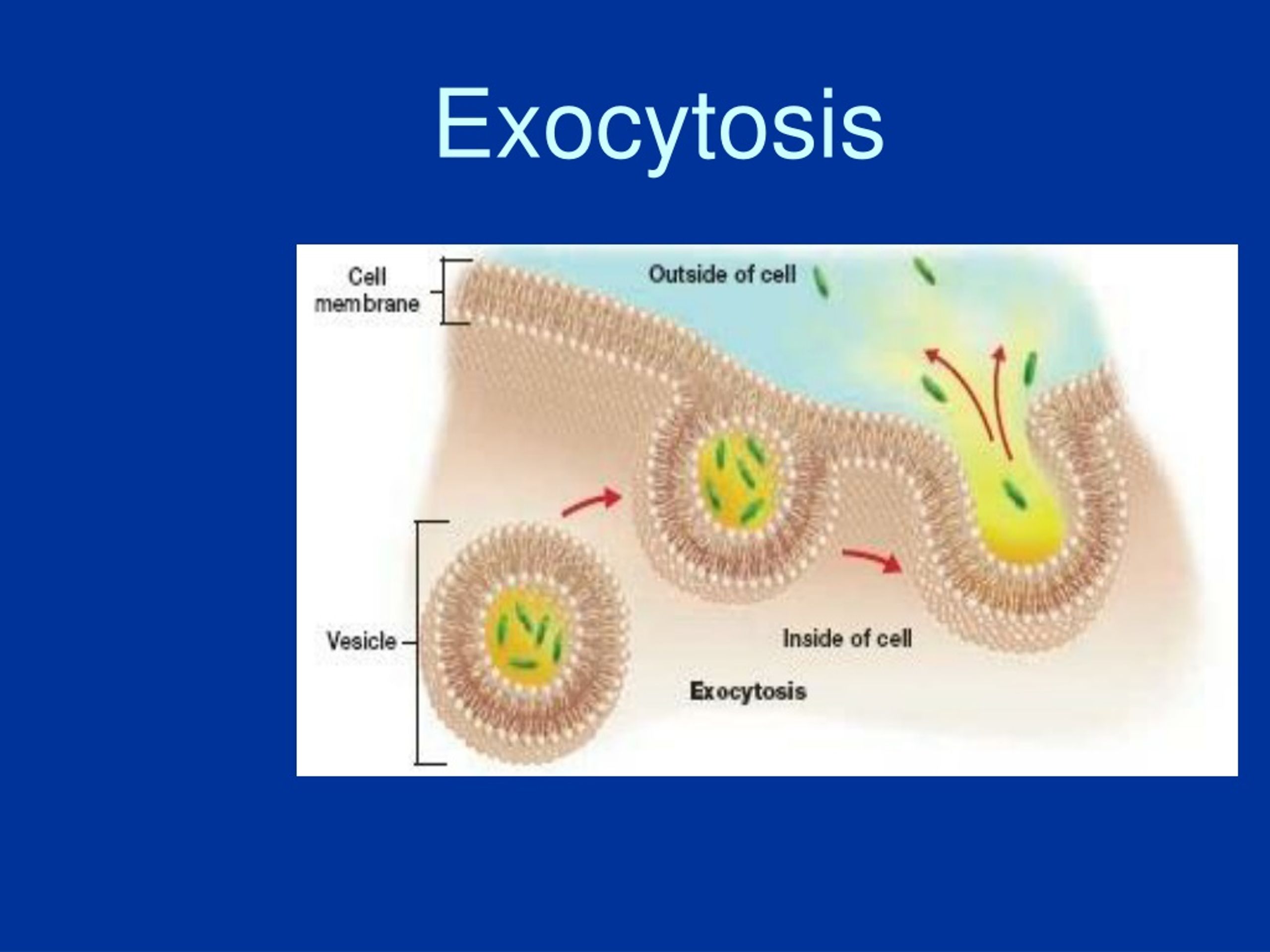
PPT Cellular Transport PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Kamalesh et al. uncover a conserved exocytic mechanism for large exocrine vesicles. Actomyosin assembly and contractility on the vesicle membrane mediates membrane crumpling and content release. Crumpling keeps the vesicular membrane sequestered from the surface, allowing for its retrieval by small endocytic vesicles, thereby maintaining cell membrane homeostasis during secretion.

Exocytosis Definition, Process, Types, Examples and FAQs
From 1952 to about 1985, exocytosis in neurons was studied mainly at neuromuscular junctions and selected giant synapses by electrophysiology and electron microscopy. Early advances were followed by a period of relative stagnation as these techniques appeared to reach their full potential. Then, in the last few years, everything changed. New methods for measuring and controlling presynaptic.
Exocytosis Types Steps And Examples
Key Terms. exocytosis: The secretion of substances through cellular membranes, either to excrete waste products or as a regulatory function; lysogenic: Of, relating to, or causing lysis.; virions: An entire virus particle, consisting of an outer protein shell called a capsid and an inner core of nucleic acid.; Viral populations do not grow through cell division because they are acellular.

What is exocytosis in a cell? examples, process, and function
5.16: Exocytosis. Exocytosis is used to release material from cells. Like other bulk transport mechanisms, exocytosis requires energy. While endocytosis takes particles into the cell, exocytosis removes them. Sometimes, the released material are signaling molecules. For example, neurons typically use exocytosis to release neurotransmitters.
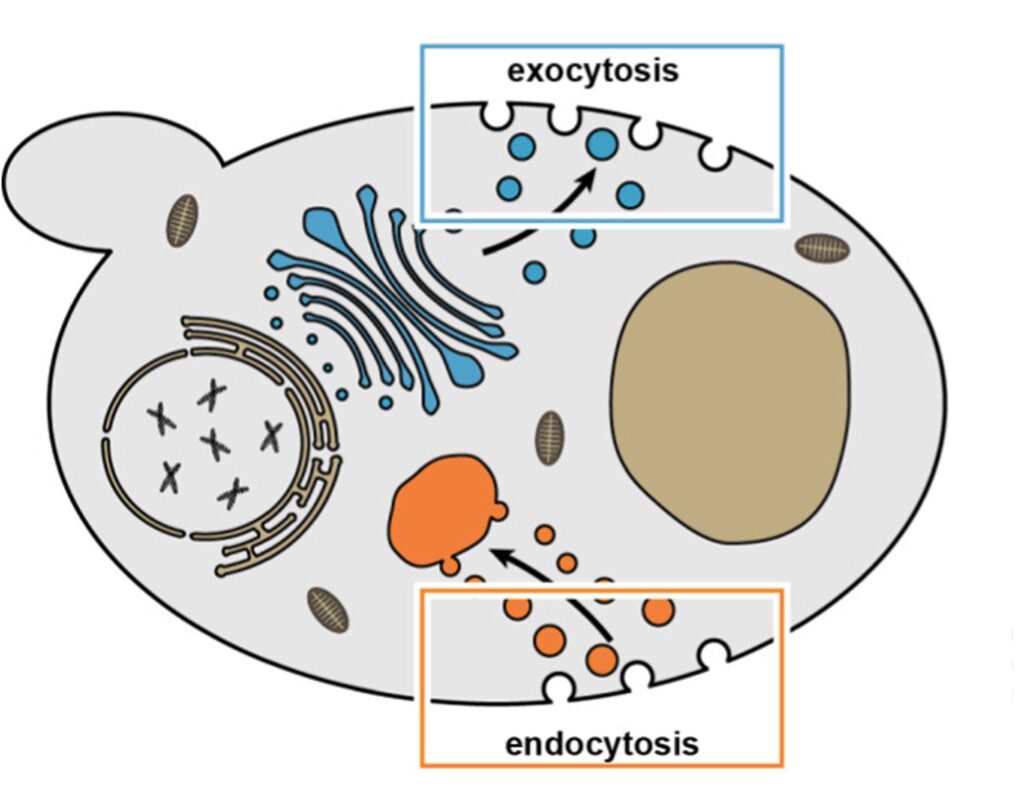
Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Similarities And Differences
Regulated exocytosis is the process by which, after an appropriate stimulus, the membrane of specific organelles fuses with and is incorporated into the plasma membrane of the cell 1.Regulated.
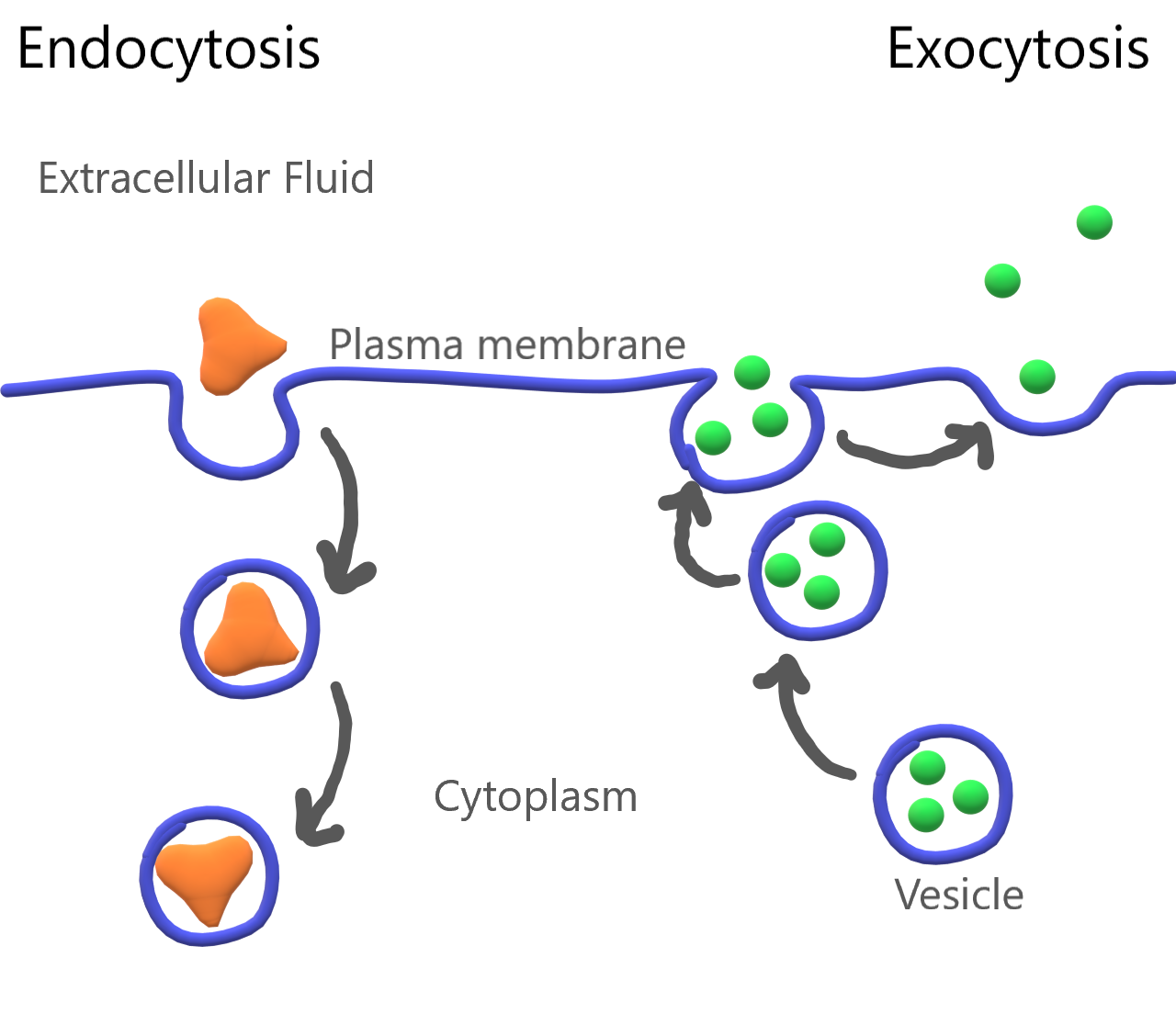
Describe Active Transport Using Protein Pumps Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Exocytosis delivers the cell membrane, cell wall materials, and signaling molecules to the apical expanding region. These results together demonstrate that the bulk of exocytosis occurs in the apical region but does not exclude the existence of exocytosis in the shoulder region for some subpopulations of exocytic vesicles (Fig. 1B).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis-582df6965f9b58d5b183203f.jpg)
A Definition of Exocytosis With Steps and Examples
Endocytosis and Exocytosis. Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane.The membrane folds over the substance and it becomes completely enclosed by the membrane. At this point a membrane-bound sac, or vesicle, pinches off and moves the substance into the cytosol.
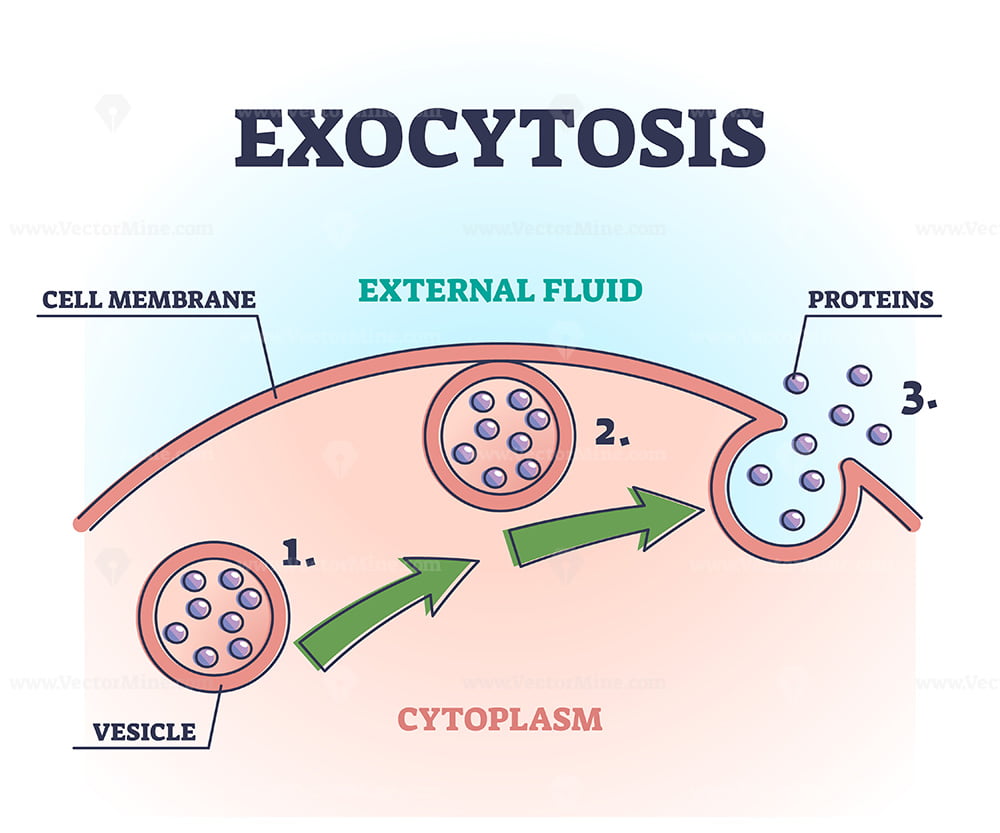
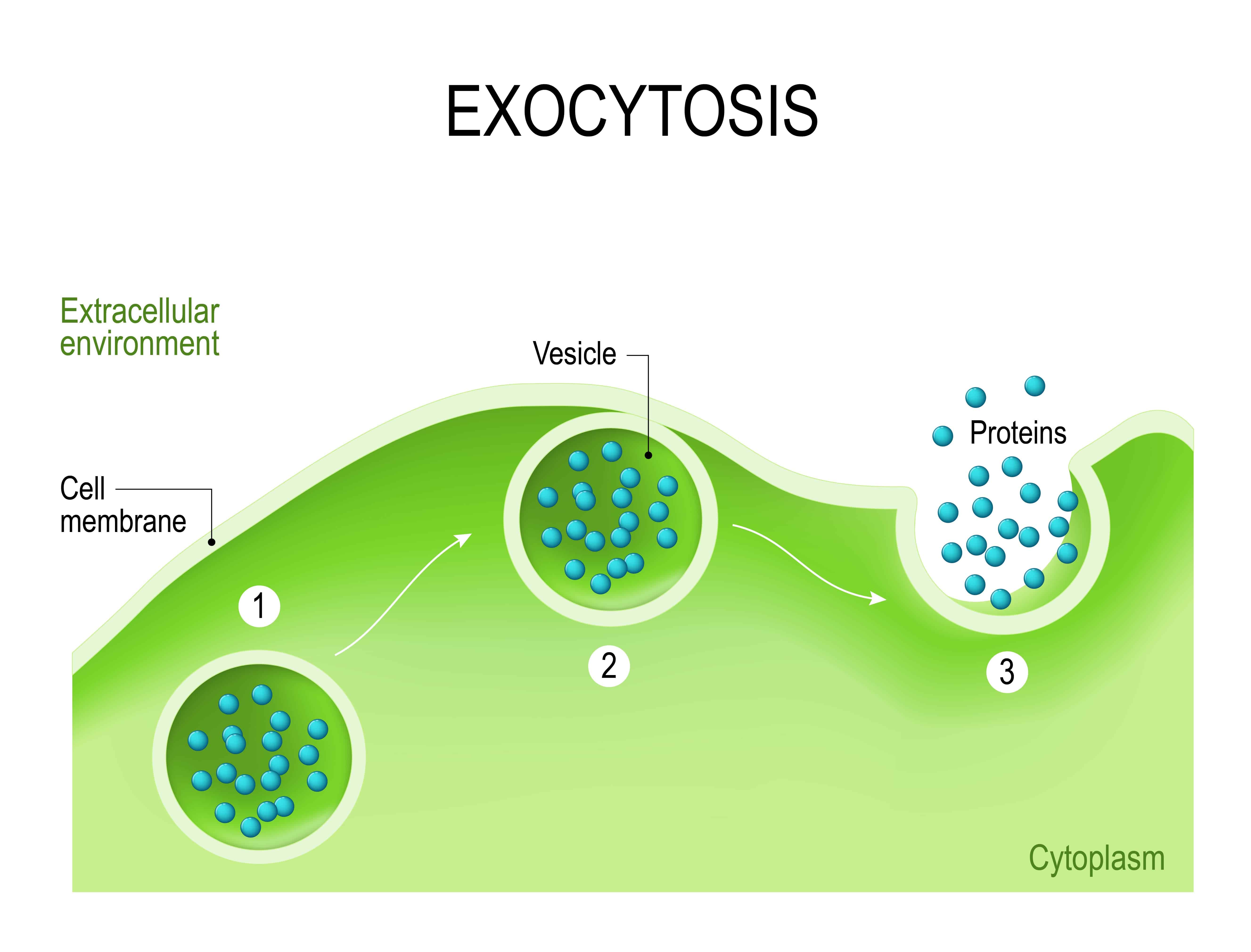
Exocytosis Types Steps And Examples
Exocytosis ( exo = external, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a form of bulk transport in which materials are transported from the inside to the outside of the cell in membrane-bound vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. Image modified from OpenStax Biology (original work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/golgi_exocytosis-5ae36c743de4230037581736.jpg)
A Definition of Exocytosis With Steps and Examples
Exocytosis. Exocytosis is a form of bulk transport during which large numbers of molecules are transported out of the cell. In exocytosis, a vesicle (a small, membrane-bound compartment) containing the molecules to be released fuses with the cell membrane, and the contents of the vesicle are expelled. Exocytosis is important for the transport.

Exocytosis Definition, Types, Steps, Examples YouTube
Regulated exocytosis is most often identified as the late step of protein and neurotransmitter secretion, consisting in the fusion between the membrane of secretory granule/ vesicle and the plasma membrane. However, a large number of nonsecretory processes, often playing key roles in cellular function, are also based on regulated exocytosis. We propose to call them nonsecretory regulated.
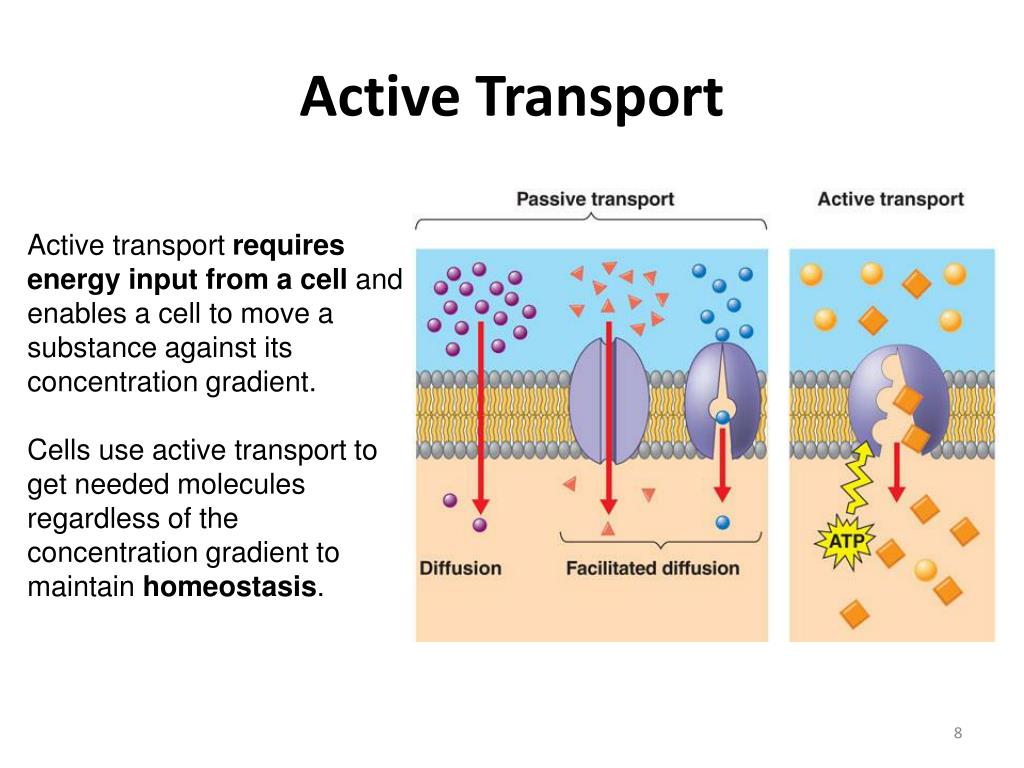
PPT Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis PowerPoint
This is true of exocytosis in eukaryotic cells, where the docking of exocytic vesicles with the plasma membrane has been shown to involve a protein complex colorfully known as the 'exocyst'. The exocyst complex comprises eight proteins: Sec3p, Sec5p, Sec6p, Sec8p, Sec10p, Sec15p, Exo70p and Exo84p. It was originally identified in the.
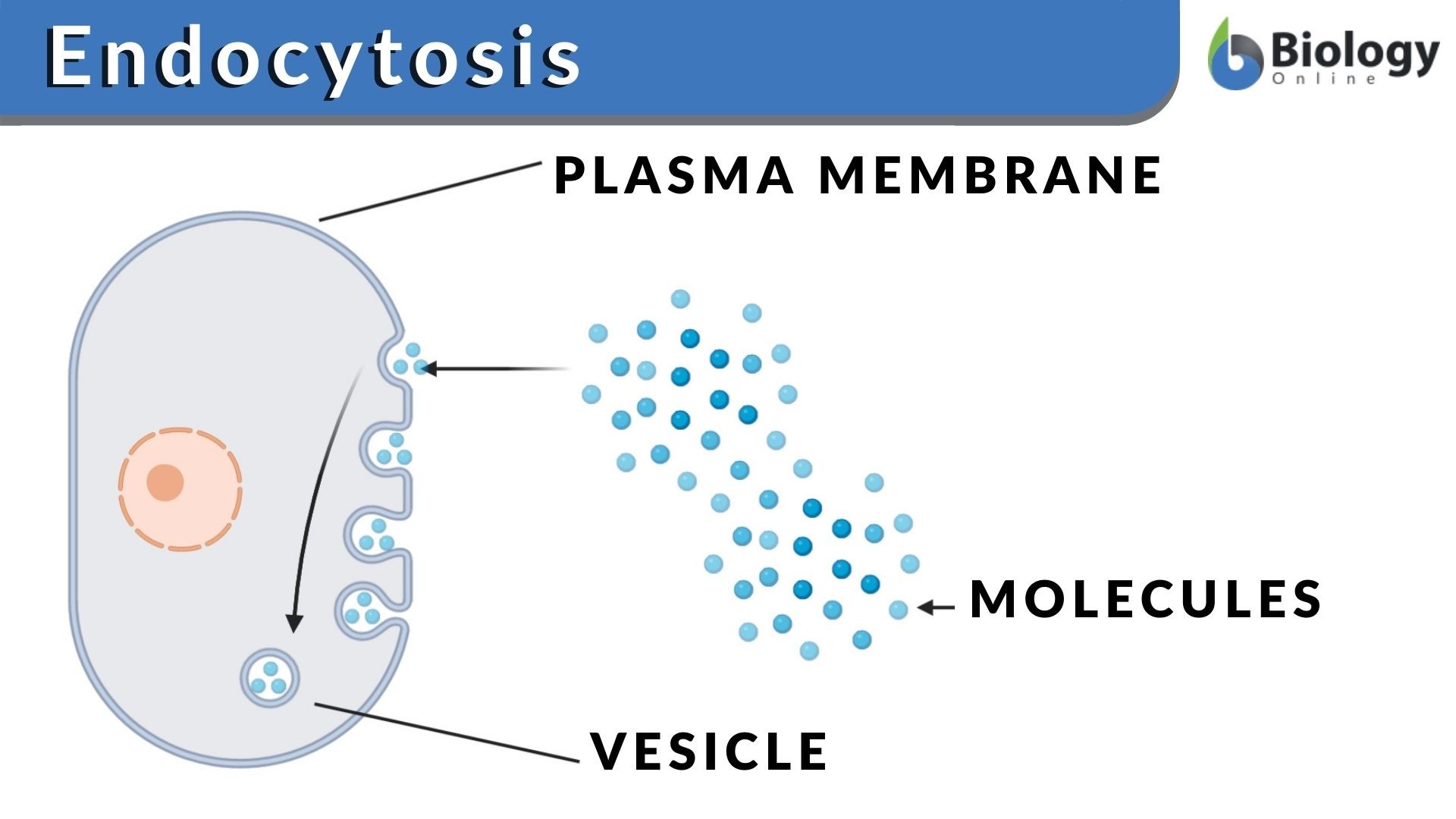
++ 50 ++ exocytosis and endocytosis 275586Exocytosis and endocytosis
Exocytosis is a general term used to denote vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane, and it is the final step in the secretory pathway that typically begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), passes through the Golgi apparatus, and ends at the outside of the cell. Endocytosis refers to the recovery of vesicles from the plasma membrane.