
Lysosome In Plant Cell Description Raine AP Biology Chapter 6 / To
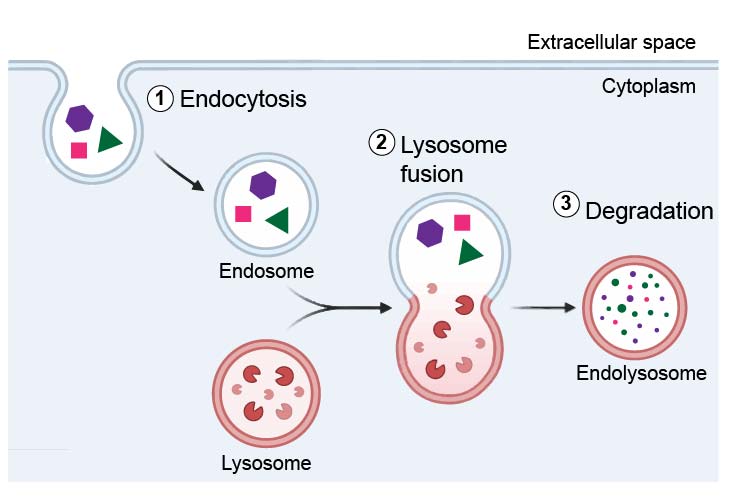
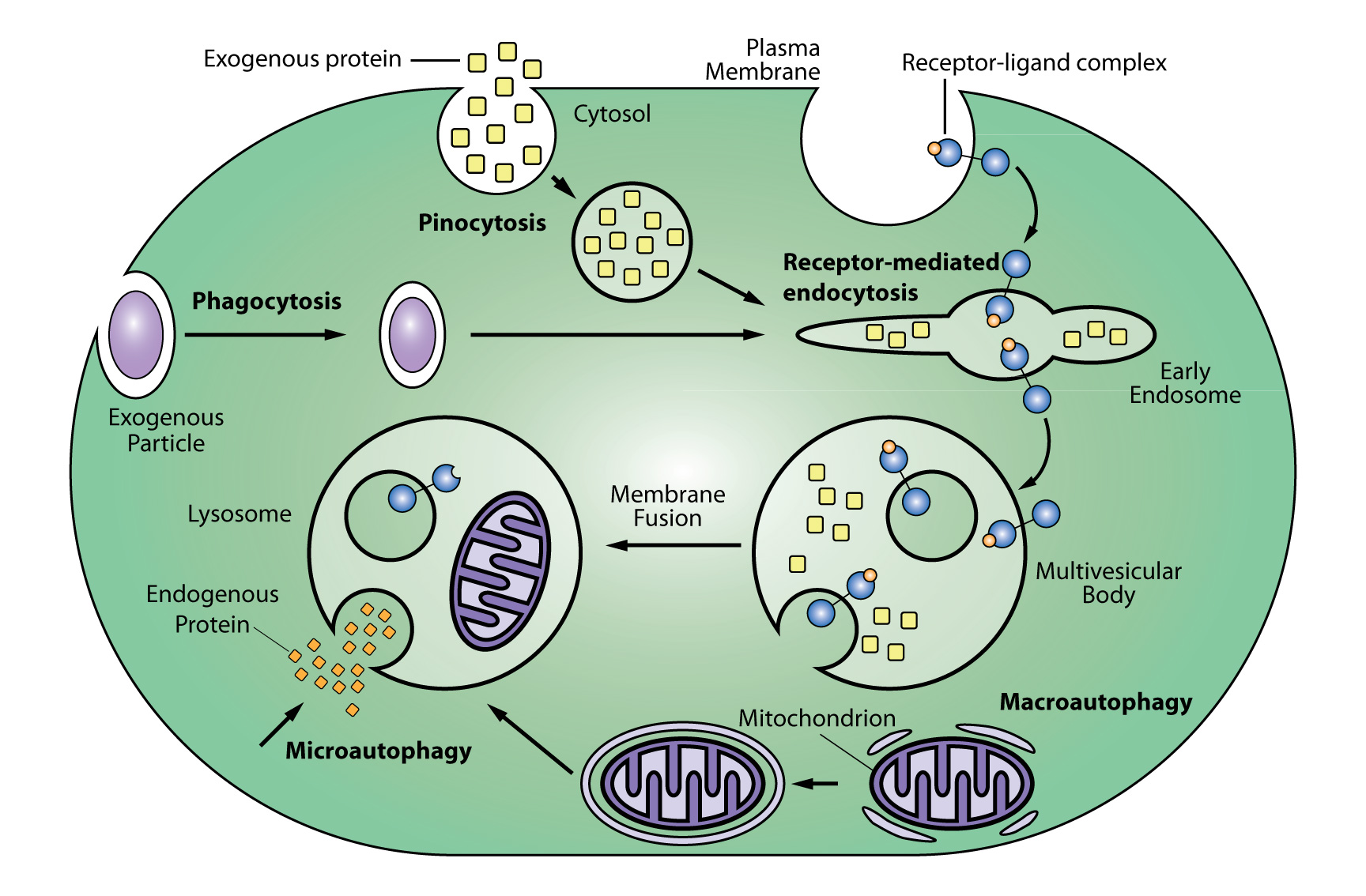
Endocytosis and Exocytosis. Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane. The membrane folds over the substance and it becomes completely enclosed by the membrane. At this point a membrane-bound sac, or vesicle, pinches off and moves the substance into the cytosol.

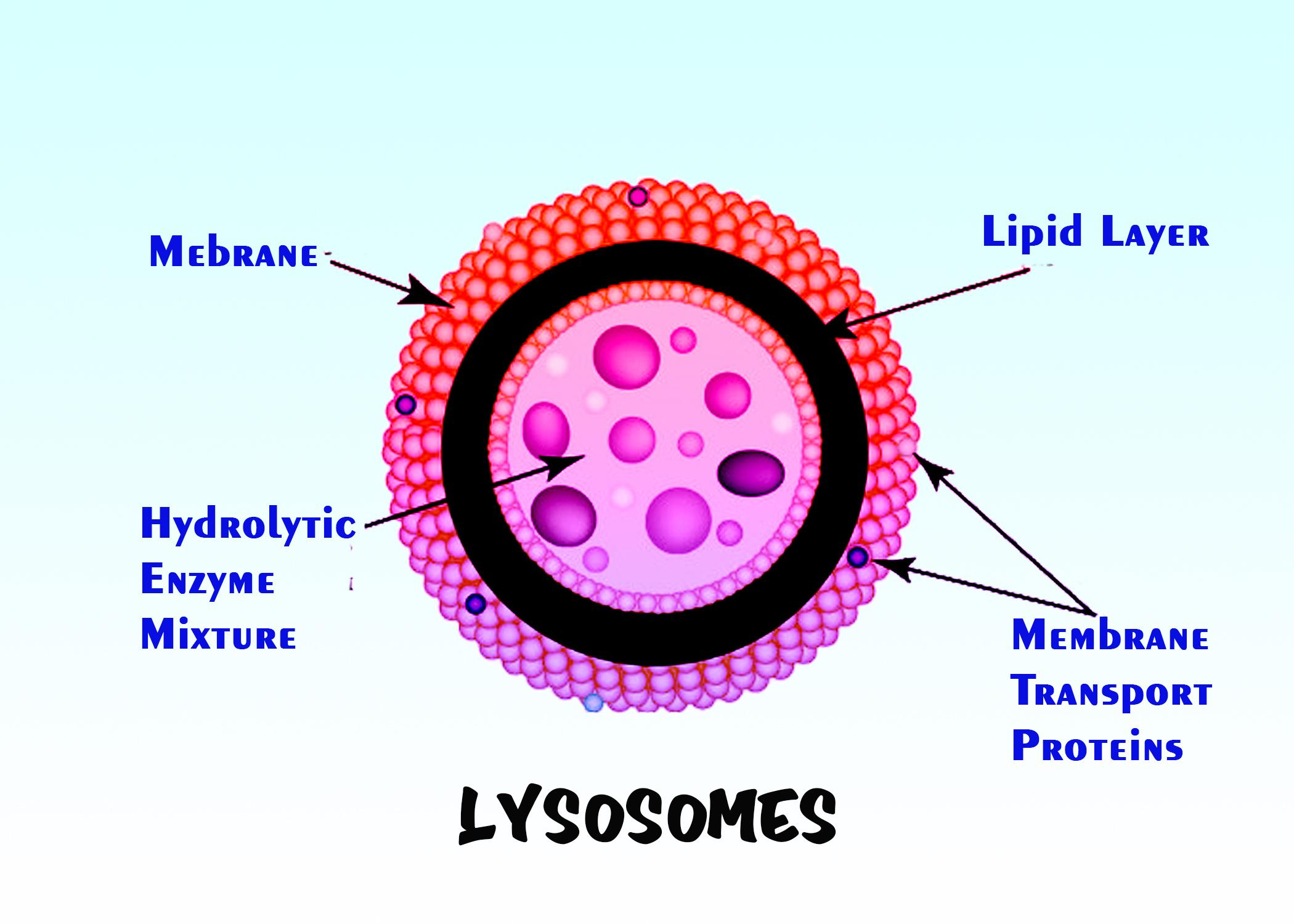
General structure and properties of lysosomes. Lysosome lipid bilayer
Structure. Lysosomes are acidic membrane-bound organelles found within cells, usually around 1 micrometre in length. Lysosomes contain numerous hydrolytic enzymes which catalyse hydrolysis reactions. The membrane surrounding the lysosome is vital to ensure these enzymes do not leak out into the cytoplasm and damage the cell from within.

Endocytosis biology Britannica
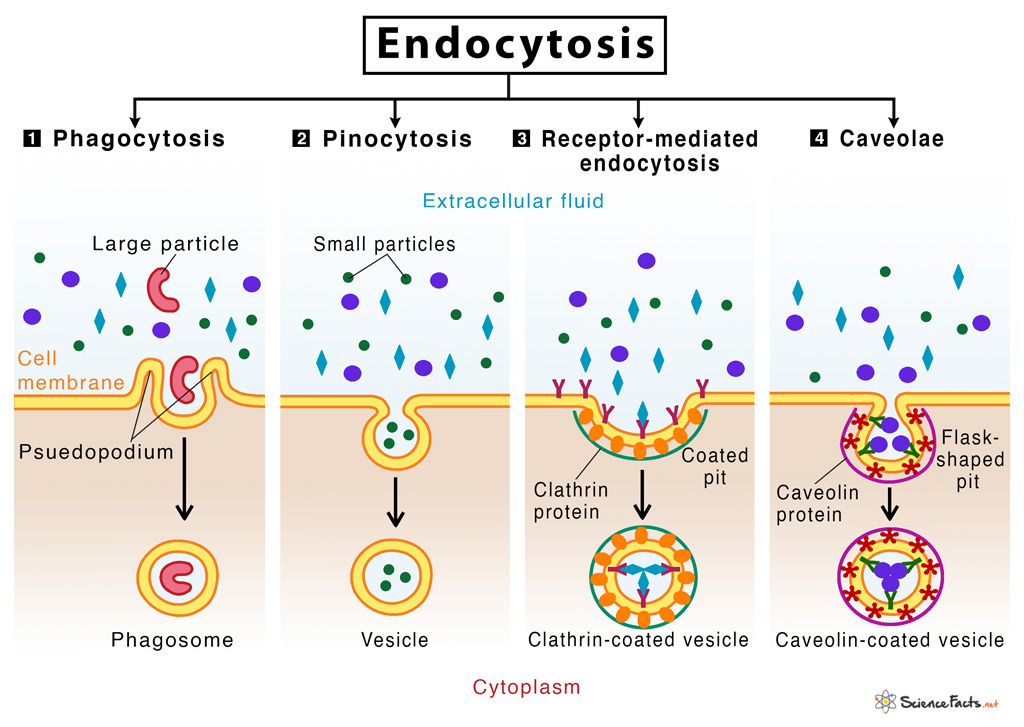
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a form of endocytosis in which receptor proteins on the cell surface are used to capture a specific target molecule. The receptors, which are transmembrane proteins, cluster in regions of the plasma membrane known as coated pits.. Macrophages have specialized compartments called lysosomes that contain enzymes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endocytosis_pinocytosis-5ad652db1f4e130038c4847b.jpg)
A Definition of Endocytosis With Steps and Types
Pinocytosis results in a much smaller vesicle than does phagocytosis, and the vesicle does not need to merge with a lysosome (Figure 2).. Cells perform three main types of endocytosis. Phagocytosis is the process by which cells ingest large particles, including other cells, by enclosing the particles in an extension of the cell membrane and.
Lysosome the cell’s recycling center definition, structure

Role of Endosomes and Lysosomes in Human Disease
In addition, CTLA-4 can enter the cytoplasm for lysosomal degradation via endocytosis [115, 116]. Lysosomes containing CTLA-4 can be transferred to the T cell receptor (TCR), which subsequently secretes CTLA-4, increasing cell surface CTLA-4.. In addition, lysosomes perform an important role in antigen presentation.

Four main types of endocytosis and a proposed exocytosis involving
This means the amount of molecules entering the cell by endocytosis is equal to the amount of molecules exiting the cell via exocytosis. The two processes combined ensure there is a balance of nutrients and waste for regular cell life and function. Necessary components in the endocytic pathway are early endosomes, late endosomes, and lysosomes.
Endocytosis Definition, Types, & Examples with Diagram
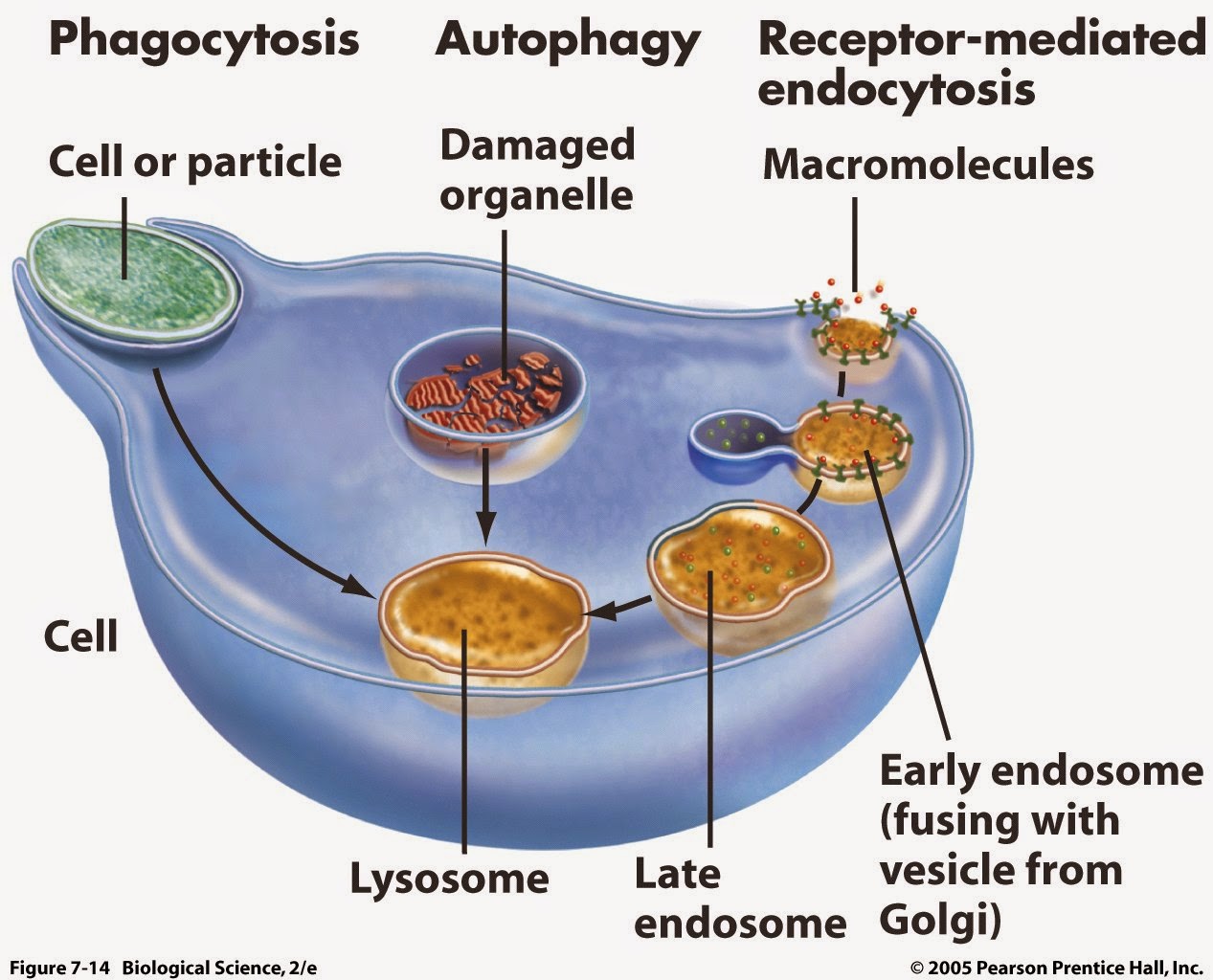
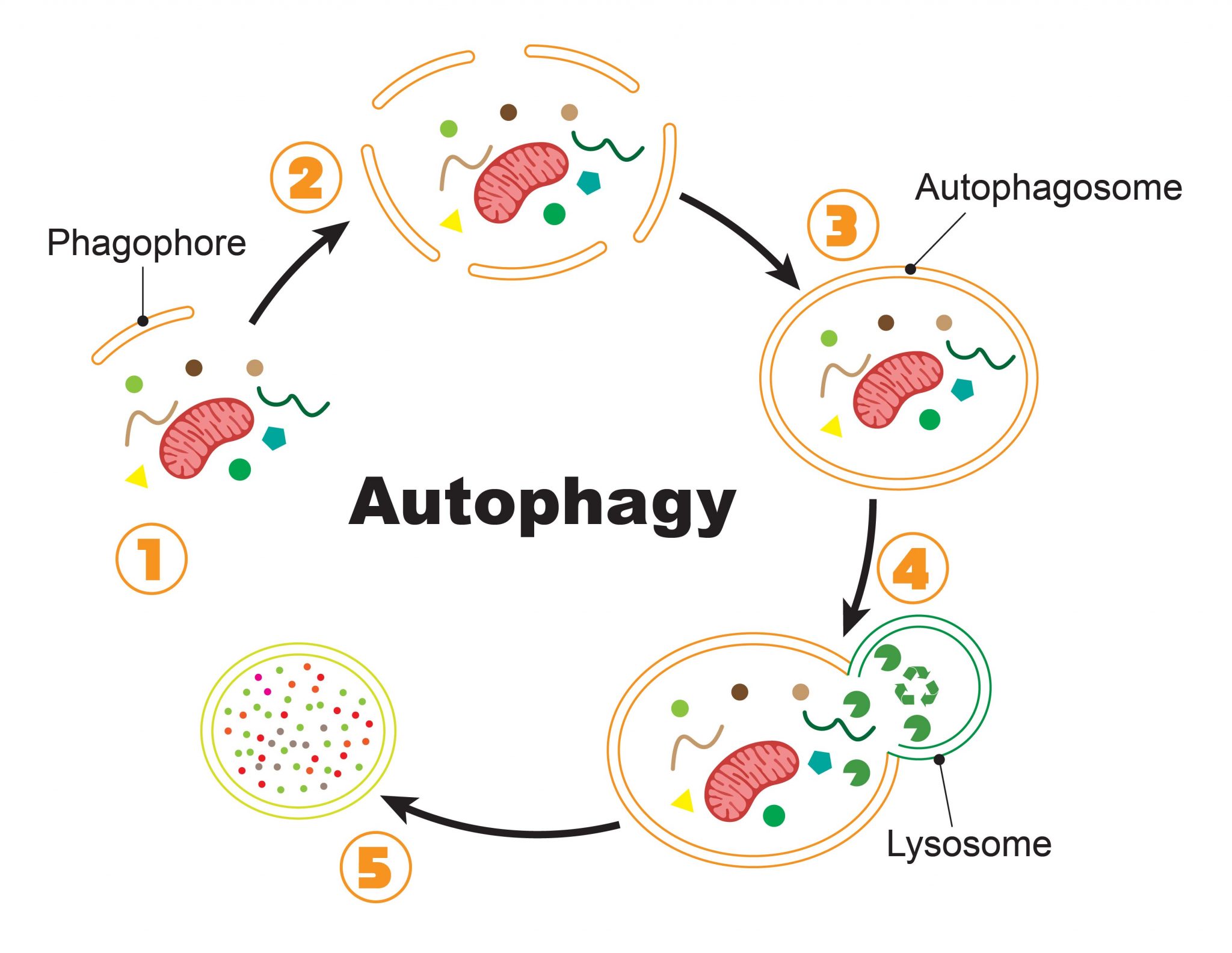
Lysosomes are versatile organelles that can associate with several other cell compartments, resulting in a variety of functions including roles in autophagy, endocytosis, phagocytosis, secretory.

STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF LYSOSOMES
Endosomes and lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles crucial for the normal functioning of the eukaryotic cell. The primary function of endosomes relates to the transportation of extracellular material into the intracellular domain. Lysosomes, on the other hand, are primarily involved in the degradation of macromolecules. Endosomes and lysosomes interact through two distinct pathways: kiss.
Marin Science Seminar All About Lysosomes
Lysosomes are highly dynamic membrane-bound organelles that act as the terminal degradative compartment of the endocytic, phagocytic and autophagocytic pathways (Fig. 1).Many of the proteins required for protein sorting and endocytic delivery to lysosomes in mammalian cells are orthologues of those used by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae for delivery to the vacuole (the yeast equivalent of.

lysosome Description, Formation, & Function Britannica
lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of macromolecules, old cell parts, and microorganisms. Each lysosome is surrounded by a membrane that maintains an acidic environment within the interior via a proton pump. Lysosomes contain a wide variety of hydrolytic enzymes.

Lysosomes Are Membranebound Vesicles That Arise From
The lysosome is an organelle that contains digestive enzymes and acts as the organelle-recycling facility of an animal cell. It breaks down old and unnecessary structures so their molecules can be reused. Lysosomes are part of the endomembrane system, and some vesicles that leave the Golgi are bound for the lysosome.
Lysosome the cell’s recycling center definition, structure
ROLE OF ENDOCYTOSIS AND LYSOSOMES 425 do, in fact, participate in endocytic uptake, but are continuously recycled or shuttled back to the cell surface. As pointed out by Steinman et al. (1976), the very magnitude of membrane interiorization makes the hypothesis of recycling almost mandatory. Our findings on the uptake of IgG by fibroblasts.

NIH scientists discover key pathway in lysosomes that coronaviruses use
Endocytosis plays a role in cell nutrition through the nonspecific uptake of various macromolecules that are conveyed to lysosomes to be digested, thus providing the cell with amino acids, carbohydrates, and lipids as energy sources or for biosynthetic purposes. Endocytosis has been tentatively divided into several categories on the basis of.
Organelles Mind Map
1. Introduction. Endocytosis is a mechanistic process, associated with internalization of the extracellular materials such as microbes, cellular components, nutrients, or macromolecules [].Conventionally, eukaryotic cells use the endocytosis process for the absorption of molecules and secretion of signaling transmitters (hormones and cytokines) to maintain cellular homeostasis [].
About the Endosomal Pathway
A lysosome is composed of lipids, which make up the membrane, and proteins, which make up the enzymes within the membrane. Usually, lysosomes are between 0.1 to 1.2μm, but the size varies based on the cell type. The general structure of a lysosome consists of a collection of enzymes surrounded by a single-layer membrane.